Industrial PCB Design and Standard
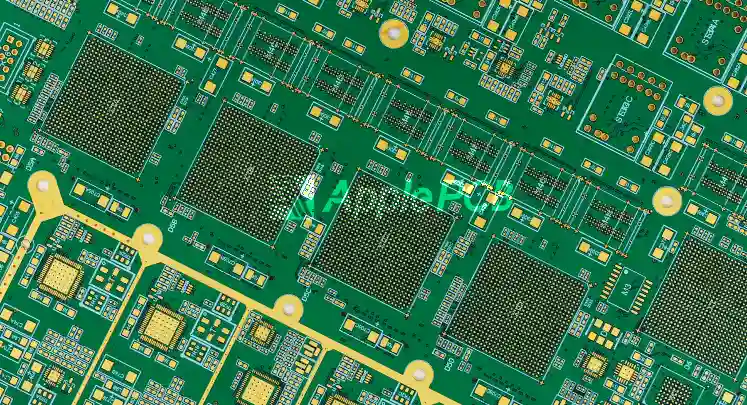
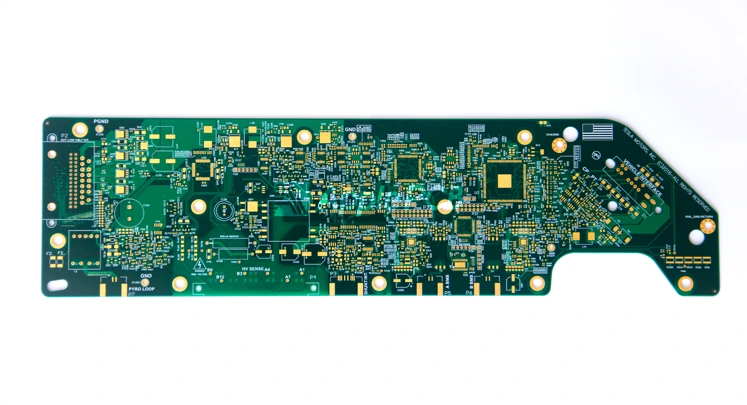
In the world of automation, the industrial pcb is the undisputed nerve center. But here is the catch: a lot of people think an industrial board is just a "sturdier" version of a commercial one. It’s not. While it might not
Read moreThings You Should Know About Through Hole PCB
In the fast-paced world of electronics manufacturing, the focus is often on "smaller, thinner, and more precise, with Surface Mount Technology (SMT) seemingly taking over. However, when it comes to high-power components or me
Read moreThe Guide to Medical PCB Standard and Design
Why Are Medical PCBs So Unique? Medical PCBs specifically refer to printed circuit boards used in medical devices and instruments. They serve as core components in equipment such as monitors, ventilators, and implantable pace
Read moreUnderstanding PCB Coverlay
In today's landscape of pervasive flexible circuits and rigid-flex boards, circuit design must prioritize not only manufacturability but, crucially, reliability. Unlike conventional rigid PCBs, flexible circuits are constantl
Read morePCB Etching Process: How to Choose Between Dry and Wet Etching?
In PCB manufacturing, if circuit design serves as the blueprint that gives a board its function, then PCB etching is the precise "sculpting" process that brings that design to life. Etching is not just a simple corrosion; it
Read moreA Comprehensive Guide to IC Substrates
With the emergence of advanced packaging technologies like chip-scale packages (CSP) and ball grid arrays (BGA), the demand for IC substrates has surged. For electronic engineers and designers, it’s no longer enough to simp
Read moreComprehensive Guide to PCB Test Points
A test point on a PCB is an exposed metal contact on the outer layer, connected to a network within the circuit. It provides a convenient spot for measuring or probing signals, power, or connections during both production and
Read moreWhy Is Trace Width So Important for PCB?
In PCB design, trace width and spacing—these seemingly simple design elements—are often overlooked. Yet they profoundly impact the product. An improper trace design can not only lead to unstable board performance but also
Read moreWhy Is Automated Optical Inspection Important for PCBs?
In the PCB manufacturing industry, you’ve probably heard the term "AOI" quite often. At first, you might think it’s just another complex technical term. But in reality, Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) is like a vigilan
Read moreMCPCB Manufacturing: Key Technologies and Advancements
In electronic designs that prioritize higher power density and reliability, the capacity of thermal management is often a key bottleneck. The low thermal conductivity of traditional FR4 PCBs (0.3 to 0.4 W/mK) often falls shor
Read more